Which Are the Types of Radiographic Projection
Lateral projections or side views. Terms in this set 16 Posteroanterior PA projection.

The Skull Clark S Positioning In Radiography By A S Whitley
Central ray passes perpendicular to the coronal plane from anterior to posterior.
. FIG 3-4 Radiographic views. Continuousspectrum of EM radiation is produced by abrupt deceleration of charged particles Bremsstrahlung is German for braking radiation. Projection X-ray imaging consists of three closely related technologies.
A difference between them can be stated in terms of dose and image quality. Posteroanterior where it enters the back and exits the front. Projection 90 to the DP view.
Continuousspectrum of EM radiation is produced by abrupt deceleration of charged particles Bremsstrahlung is German for braking radiation. The radiographic projection in which the x-ray beam enters the posterior side and exits to the film through the anterior side. EXTRAORAL RADIOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUES- 7.
Projection Radiography Yao Wang NYU 10. Posteroanterior where it enters the back and exits the front. Bitewing Radiography was introduced by Howard Raper in 1924.
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI. Are those in which the is rotated so that the CR travels through the body on an oblique plane rather than following and anatomic plane. Deceleration is caused by deflection of electrons in the Coulomb field of the nuclei Most of the energy is converted into heat 05.
It makes use of intensifying screens. EL5823 Projection Radiography Yao Wang NYU-Poly 8. PA posteroanterior When the central ray enters the posterior body surface and exits at the anterior body surface.
Radiography pertains to the acquisition of static two-dimensional images of nearly all body parts ranging from the main body habitus to extremities and the skull. Basic radiographic projections include anteroposterior where the X-ray beam enters the front of the body and exits through the back. In plain radiography X-ray anteroposterior and lateral hip radiographs are usually taken.
Medial rotation or lateral rotation. Anteroposterior lateral oblique and posteroanterior. Anteroposterior - The radiographic projection in which the x-ray beam enters the anterior side and exits to the film through the posterior side.
Continuousspectrum of EM radiation is produced by abrupt deceleration of charged particles Bremsstrahlung is German for braking radiation. EL5823 Projection Radiography Yao Wang NYU-Poly 9. The CR central ray enters the posterior surface and exits at the anterior surface.
AP anteroposterior When the central ray enters the anterior body surface and exits at the posterior body surface. In the Radiology Emergency Department of our hospital a. What are the types of radiographic projection.
Radiography mammography and fluoroscopy. Non invasive xray procedure uses an external magnetic field to produce a two dimensional view of an internal organ or structure such as the brain or spinal cord. Central ray passes perpendicular to the coronal plane from posterior to anterior.
And oblique projections where the body is positioned at a 45-degree angle relative to. Xray of a joint after injection of contrast material. The following projections were obtained in sequence.
Some types are used to view the entire skull whereas other types focus on the maxilla and mandible. Radiographic positioning is the physical position of the body being imaged and radiographic projections are the beams that provide visuals when computed. In projection radiography two types of digital imaging systems are currently available computed radiography CR and direct radiography DR.
Demonstrates the metatarsals in the natural anatomical position. The direction or path of the. A DP projection with the foot angled 30-40 medially depending on the transverse arch the most pertinent projection for the evaluation of the tarsal bones that form the midfoot and forefoot structures 13.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. The radiographic projection in which the x-ray beam enters the anterior side and exits to the film through. Mammography extends that application to be specific for breast.
Deceleration is caused by deflection of electrons in the Coulomb field of the nuclei. Which are the types of radiographic projection. AP or PA oblique projections.
Deceleration is caused by deflection of electrons in the Coulomb field of the nuclei Most of the energy is converted into heat 05 is x-ray The energy of the. For example A denotes an anteroposterior AP projection and B a posteroanterior PA projection. Cephalometric and skull views require at least a 8X10 inch image receptor whereas oblique lateral projections of the mandible can be obtained with 5X7 inch.
STANDARD RADIOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUES. Bitewing Radiographs could be categorised into 3 types of projections namely anterior projection for incisor canine teeth premolar projection for premolar. In the extremities lateral projections are similarly described by the direction of the central ray.
Lateral position - Position in which the body is on the side at 90 degrees or perpendicular or at a right angle to a true AP or PA projection. An anteroposterior hip radiograph includes images of both sides of the hip on the same film and projects towards the middle of the line connecting the upper symphysis pubis and anterior-superior iliac spine. The CR central ray enters the anterior surface and exits at the posterior surface.
Explore the terms associated with both of. Oblique at 45 or 30 angle on inspiration oblique at 45 or 30 angle on expiration as well as 45 and 39 projections during slow and fast breathing. Eight different plain radiography pictures of ribs were performed with the patient in an erect position.
Projection Radiography Yao Wang NYU 9. The term radiographic projection references the path of the central ray as it exits the x-ray tube and passes through the patients body. Basic radiographic projections include anteroposterior where the X-ray beam enters the front of the body and exits through the back.
Are radiographs taken with a longitudinal angulation of the CR of 10 degrees or more.

Radiographics Positioning Projections Terminology Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

A Lateral Radiographic Projection Of The Subject And Control Tibia Download Scientific Diagram

Radiographic Positioning Image Analysis 5th Edition X Ray Lady Analysis Free Books Online Workbook
Projection X Ray Imaging Radiology Key
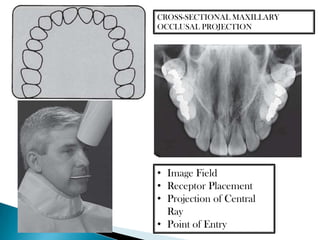
9 Extraoral Projections And Anatomy Pocket Dentistry

Extraoral Radiographic Projections Topics In Description Below Youtube

Bontrager S Handbook Of Radiographic Positioning And Techniques By John Lampignano

Craniocaudal A And Mediolateral B Radiographic Projection Of A Download Scientific Diagram

Ppt Radiographic Projection Of Objects Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5370062
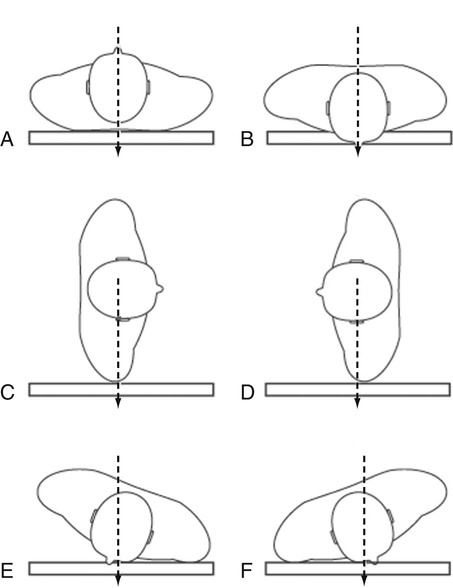
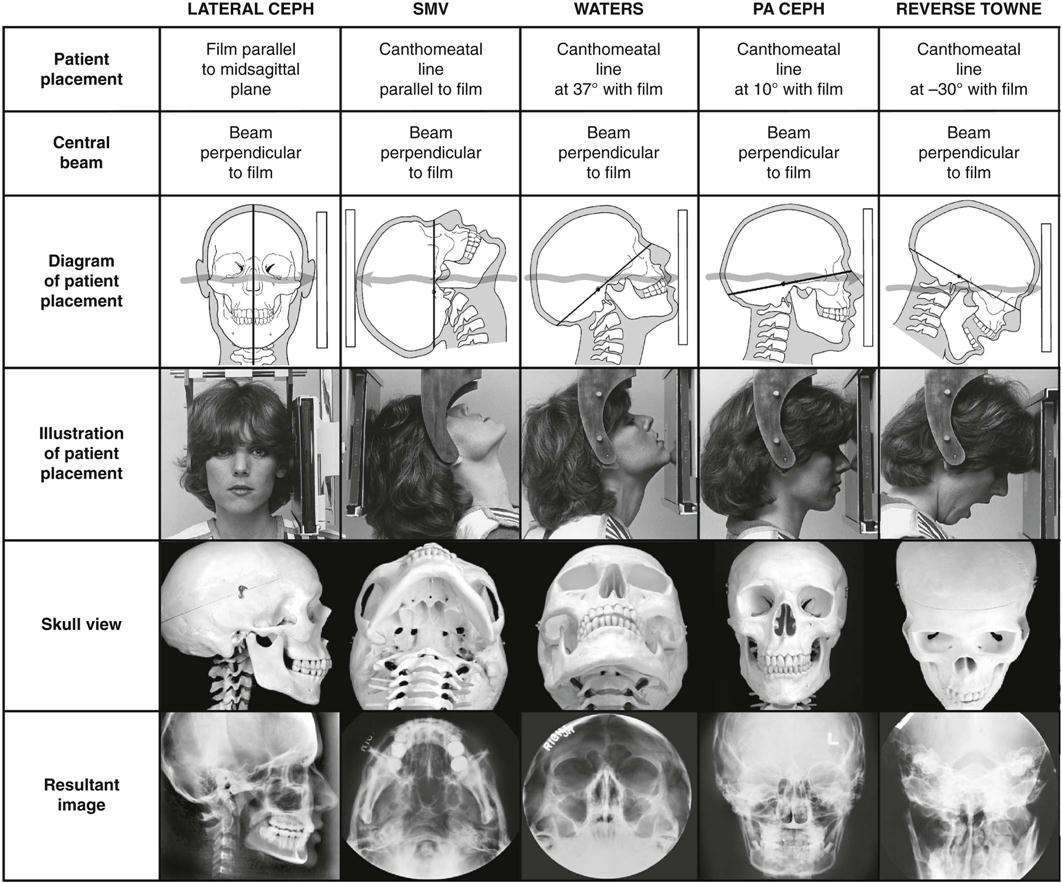
Radiographic Positioning Radiology Key

Radiographic Positioning By Olive Peart Ebook Scribd

Lateral Radiographic Projection Showing The Preoperative View Download Scientific Diagram
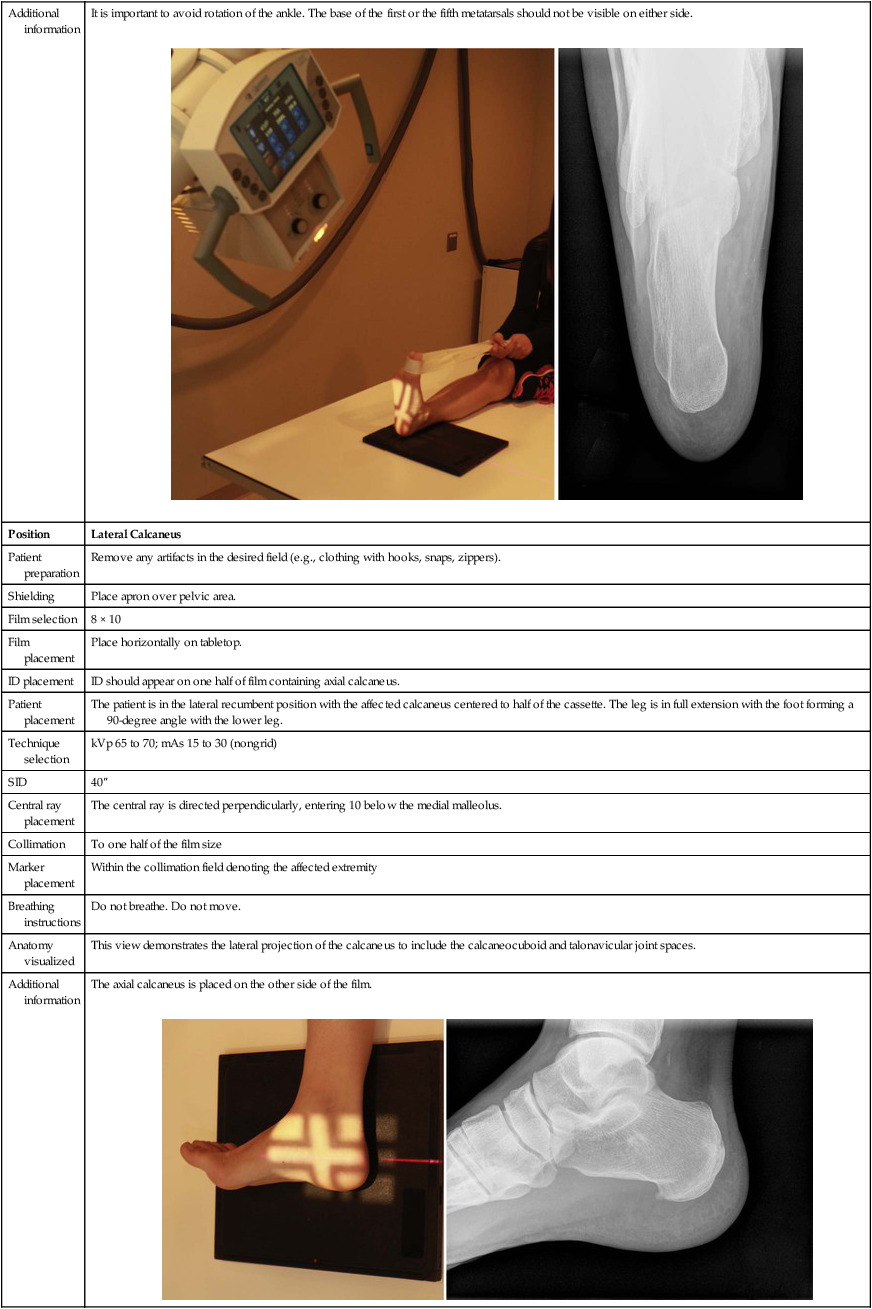
Radiographic Positioning Radiology Key
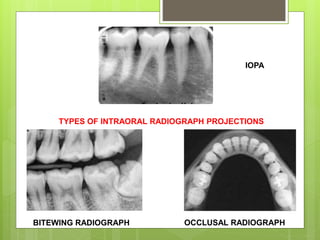
Paralleling And Bisecting Radiographic Techniques

Radiographic Positioning Head Shoulders Knees Toes Part 2 Today S Veterinary Nurse
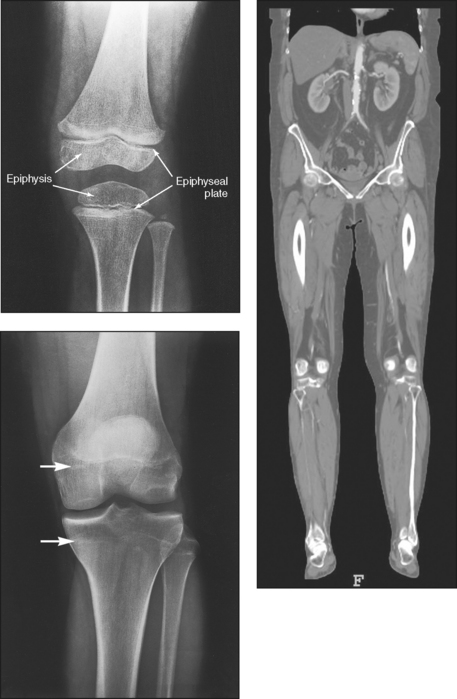
General Anatomy And Radiographic Positioning Terminology Radiology Key
Ppt Introduction Of Radiographic Technology Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 1307807
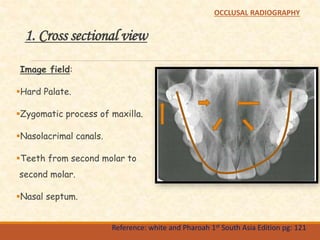
Comments
Post a Comment